Diagnostic Testing
Enhance your sight today! Call or book your appointment now to unlock premier vision…
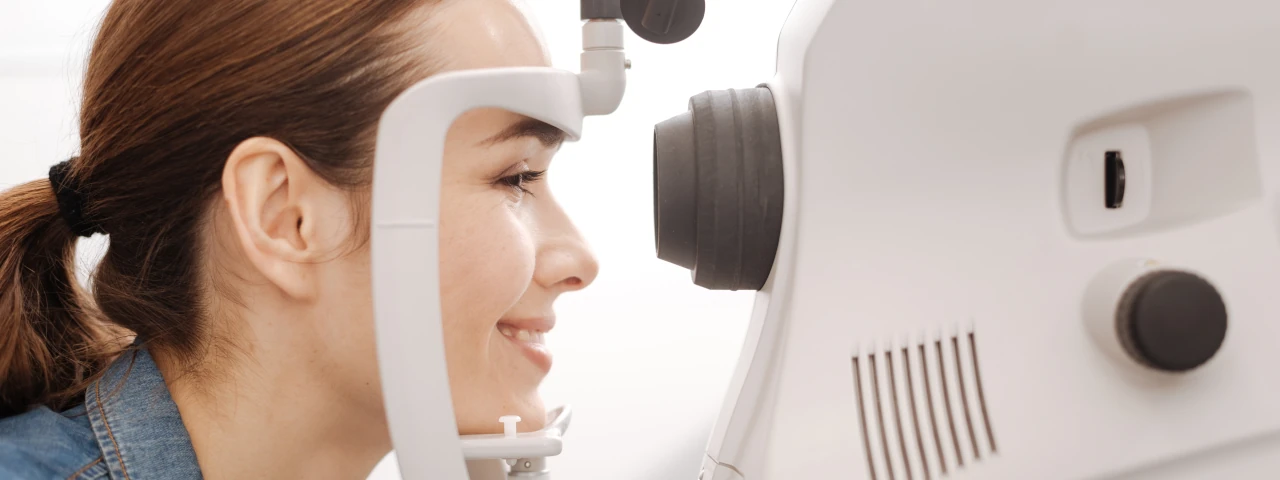
VISUAL FIELDS
The Visual Field test is a measurement of the peripheral or side vision. It is important in testing for eye diseases such as glaucoma, retinal problems, and other problems such as brain tumors or damage from certain medications which can build up in the body. This test is also instrumental in showing visual improvement for medically necessary eyelid surgery.
HUMPHREY VISUAL FIELD
This field test is a computerized threshold perimetry, which reports the sensitivity to light at a given location and converts into patterns in shades of gray. Each time the patient sees a light a button is pushed and is documented by the computer. Areas of normal appear white and the shades become increasingly gray as sensitivity is reduced. Black indicates areas of total loss.
GOLDMAN VISUAL FIELD
The patient is seated in front of a lighted screen set at certain levels with one eye patched. The technician moves a handle attached to a projector from outside the patient’s vision toward the center until the patient sees the light. The patient indicates seeing the light by pushing a button. The technician plots the point on the visual field results indicating where vision is present. This test is often used to show visual improvement with the eyelids taped and untaped for medically necessary eyelid surgery.
VISUAL FIELD FEATURES AND BENEFITS
- Printout of each patient’s individual test results
- Pinpoints areas of abnormality and documents accordingly
- Detects and documents if the patient has any visual field abnormalities and to what degree
- Monitors any changes in the visual field from year to year
- Accurate mapping – identifies the nature and location of a disease.
OPHTHALMOSCOPY
Ophthalmoscopy is a method of examining the back of the eye in great detail, using a special lens. It requires the patient’s eye be dilated. The doctor will then make a detail diagram of any abnormalities so that this can be followed from visit to visit and document any changes in the eye.
OPHTHALMOSCOPY FEATURES AND BENEFITS
- Detailed diagram
- Doctor is able to draw an exact drawing of the back of the eye while the patient is in exam room
- Any changes are able to be detected from year to year
GONIOSCOPY
A special viewing method in which a lens with a mirror is placed in front of the eye to enable the doctor to examine a part of the eye which could not otherwise be seen. This is helpful in patients who have glaucoma or high pressures in the eye and allows the doctor to see the angles where the fluid of the eye drains out.
GONIOSCOPY FEATURES AND BENEFITS
- Feature: 4 mirror lens
- Benefit: Ability to detect conditions which cause glaucoma
- Benefit: Only requires topical Anesthetic
EXTERNAL PHOTOS
A method of photographing any abnormalities which allows the doctor to document any changes of the skin, face, or eyelids. It is especially helpful in documenting any blockage of vision by brows or excess skin and changes in lesions.
EXTERNAL PHOTO FEATURES
- Immediate Photo
- Portable
- Convenient
EXTERNAL PHOTO BENEFITS
- Able to ensure we have a good photo before patient leaves the office
- Able to detect any changes in patient’s skin, face, or eyelids between visits
INTERNAL PHOTOS
Method of photographing the back of the eye using a special camera with a high powered lens. It requires the patient to be dilated and is important because it documents any abnormalities which can be monitored from year to year
INTERNAL PHOTO FEATURES
- Ability to study a still fundus photo
- Magnifying adapter
- Convenience
INTERNAL PHOTO BENEFITS
- Better tracking of retinal changes – Could save vision!
- Picks up concentrated areas for microscopic changes
- Patient is already dilated – same day as regular appointment
OPD – OPTICAL PATH DIFFERENCE
With this single device doctors can obtain different measurements of the eye such as:
AUTO REFRACTION – AN OBJECTIVE MEASUREMENT OF YOUR GLASSES PRESCRIPTION
This is a computerized refraction that measures the eye multiple times to determine the most accurate prescription for glasses available today
CORNEAL TOPOGRAPHY
Provides a color detail mapping of the cornea and allows early detection of corneal disease such as Keratoconus
AUTO KERATOMETRY
Measures the corneal curvature and is crucial in determining astigmatism in patients for glasses, contact lenses and Intraocular Lens Implants
OCT – OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY
This specialized piece of equipment is used to obtain images of the retina or the optic disc, it uses laser for the measurement.
OCT – MACULAR SCAN
Progressive technology has produced a non-invasive procedure for imaging the macula. The images displayed are layers of the macula, and a mapping of the retina that provides multiple measurements for the doctor to evaluate and compare
OCT –OPTIC NERVE DISC
This is a multi-scale 3-D graph of the optic nerve that is extremely important for detecting and tracking Glaucoma. Early detection is so important because Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of blindness due to the gradual damage to the retinal nerve fiber layer
IOL MASTER
This is a non-contact (nothing touches the eye and drops are not required) highly accurate piece of equipment that measures the length of the eye for future cataract surgery needs. The Intraocular Lens power is then determined by using the length of measurements combined with the corneal curvature. The lens power and design is then chosen to best meet your individual needs
COLOR PLATES – ISIHARA OR PIP (PSEUDO-ISOCHROMATIC PLATES)
Color plates are used to determine color deficiency in patients. Patients may have been color deficient since birth, or as a result of certain medications or diseases. The test is performed one eye at a time, using a total of 14 plate, two of which can be easily seen for comparison purposes.
TONOMETRY
This test measures the intra-ocular pressure or pressure inside the eye. There are different devices that can be used for this measurement, depending on the situation. This is an important test for Glaucoma, and determines if there is a build-up of fluid within the eye. This fluid build-up can damage the eye.
REFRACTION
The glasses and/or contact lenses prescription is discovered by performing this test. During this test the doctor is able to determine if a patient is nearsighted, farsighted, presbyopic or if they have astigmatism. The technician or doctor may ask “Which lens looks better lens one or lens two… or do they appear the same?”
SCHEDULE YOUR CONSULTATION
Ask A Question or Book Your Appointment Today! This Quick Form Will Save You Time Getting Your Answers.